Cladding
Application

Application of Cladding in Industry
Corrosion-resistant alloys are often used to build equipment in the chemical, steel or oil industries. The initial cost of such equipment is much higher than that of carbon steel. This is especially the case when high temperatures and high pressures require thicker wall thicknesses for the equipment. The cost of the equipment can be significantly reduced by opting for construction using bi-metal material obtained by cladding. The explosion cladding of a relatively thin layer of a corrosion-resistant alloy (cladding) onto a lower-cost carbon steel plate (base) has proved to be an extremely advantageous and highly reliable alternative.
For many types of metal combinations, thicknesses, and technical requirements, explosion cladding means the lowest cost, highest added value solution. Commonly used clad alloys include stainless steels, nickel alloys, copper alloys, titanium, and zirconium, all of which are welded to carbon and alloy steels. Explosion cladding is a solid-state metal welding process that uses explosive energy to create a metallurgical bond between two metal components. Although the explosion generates considerable instantaneous heat, there is no time for the heat to transfer to the metal components; consequently, there is no temperature increase in the metals during welding.
Clad metals, with their rare ability to match virtually any design need, offer design engineering some highly desirable benefits. 'Clad' not only allows you to expand your design possibilities, but can also provide significant improvements in product performance and manufacturability. And above all, it means a marked reduction in product costs.
Cladding areas of activity
Oil and gas
The oil and gas sector is the basis of Brazil's energy matrix and is responsible for 15% of industrial GDP.

Heat exchanger under construction.

Drop-shaped Mirror Disc.

Heat exchanger mirror clad in naval brass.

Clad plate heat exchanger.

Various reactors.

Discs before TTAT.
Manufacturing Industry
The Manufacturing Industry is a segment of industry that transforms raw materials into a final or intermediate product that will be modified again by another industry.



Aluminum x Carbon Steel transition joints for blast furnaces.
Electrochemistry
Electrochemical processes such as galvanizing in industry protect metal surfaces, preventing corrosion of plant and machinery. We produce transition joints for the chemical industry in Steel x Copper

Electrolytic cell for chlorine soda.
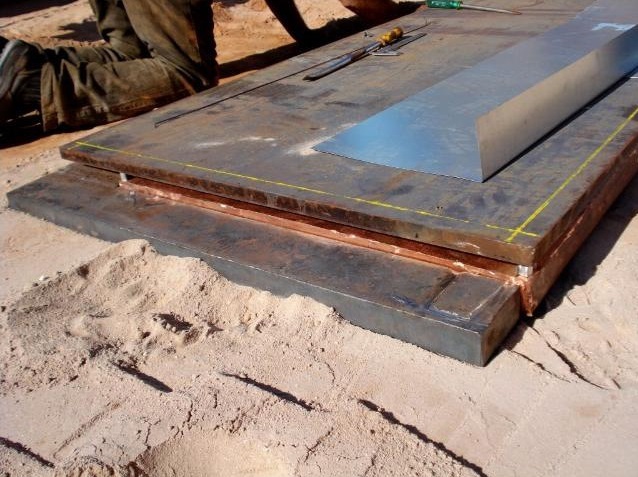

Plate on the base.
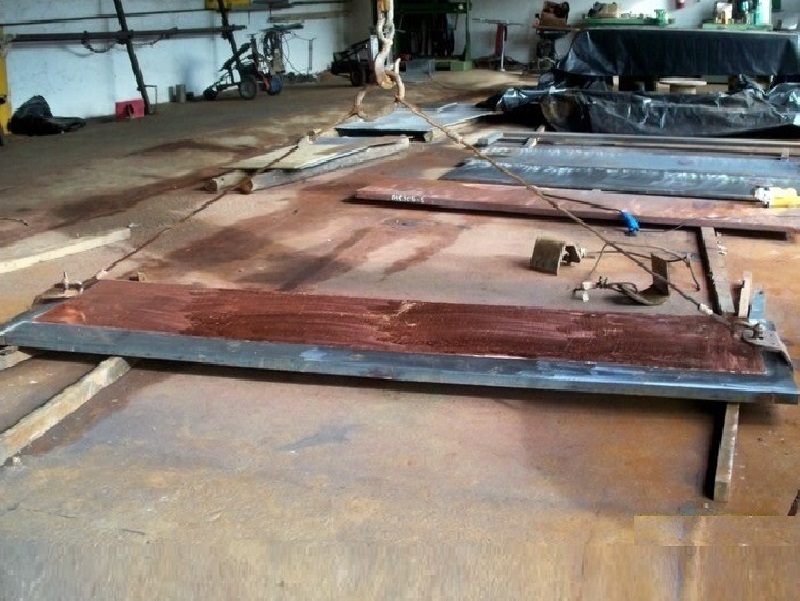

Raw sheet preparation.
Energy and Mining
The energy and mining industries supply raw materials to various segments of the economy. Steel and metallurgical plants are highly dependent on ore cargoes, which are processed and transformed into products of interest.
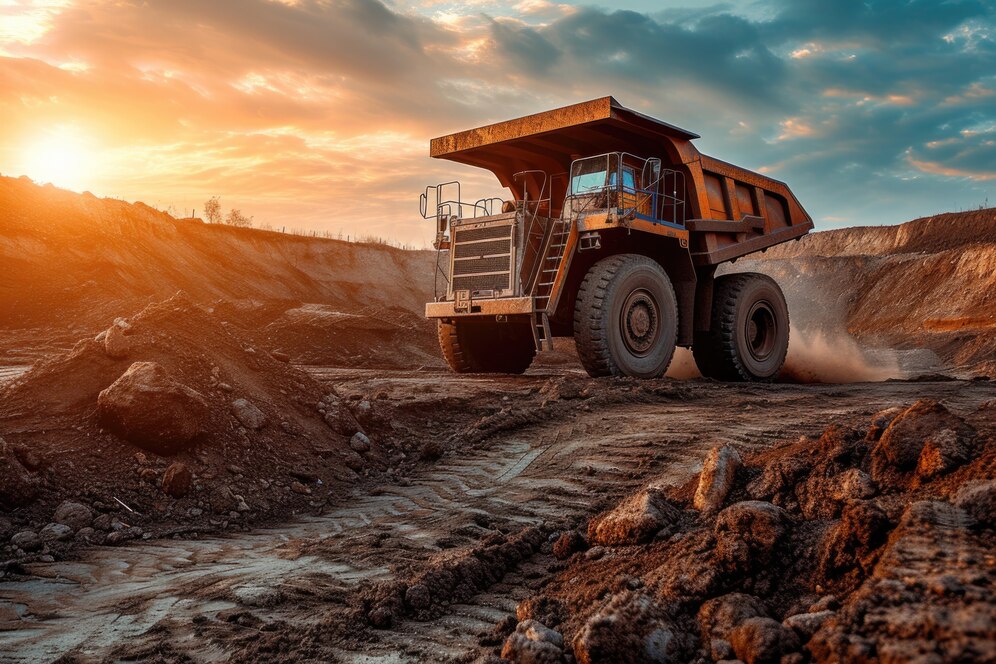

Dump Truck.
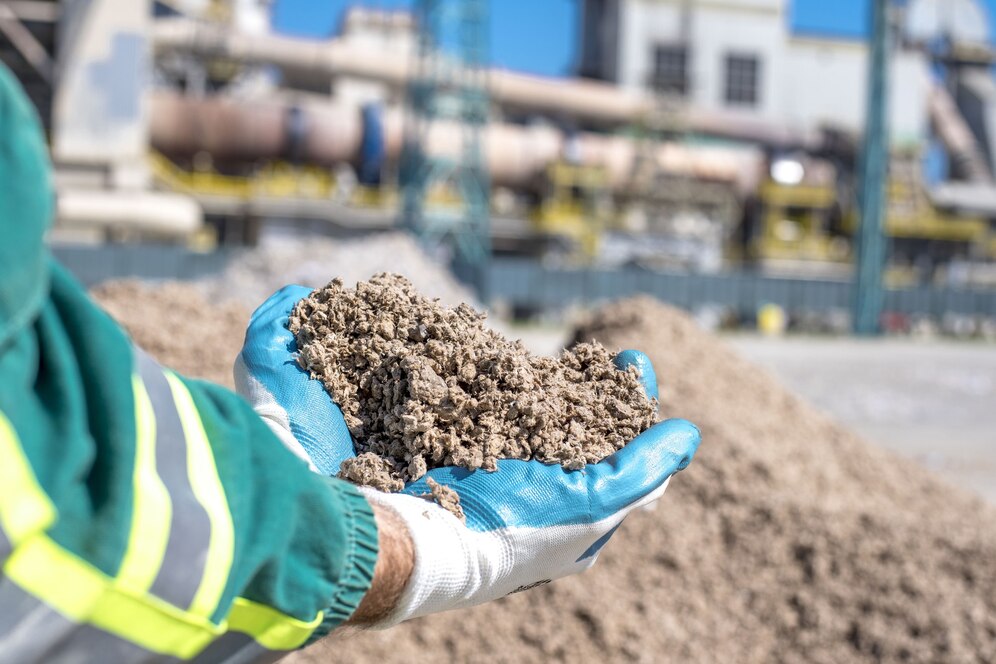

Ore treatment process.
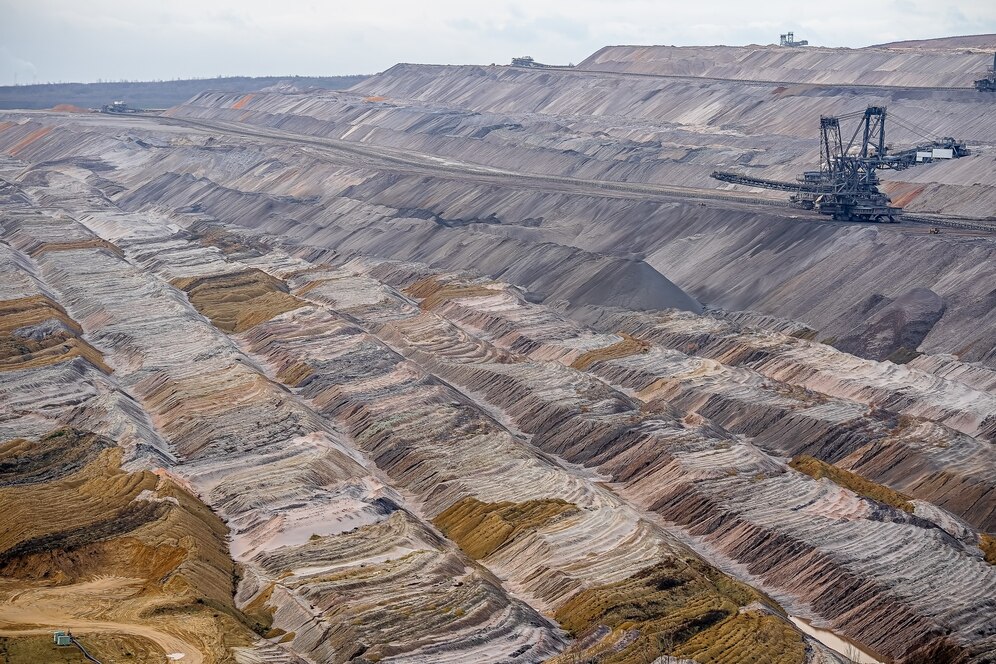

Open-pit mining.
Food industry
The food industry is a branch made up of a series of activities. It encompasses the processing, storage, transportation and marketing of ingredients and other food products.
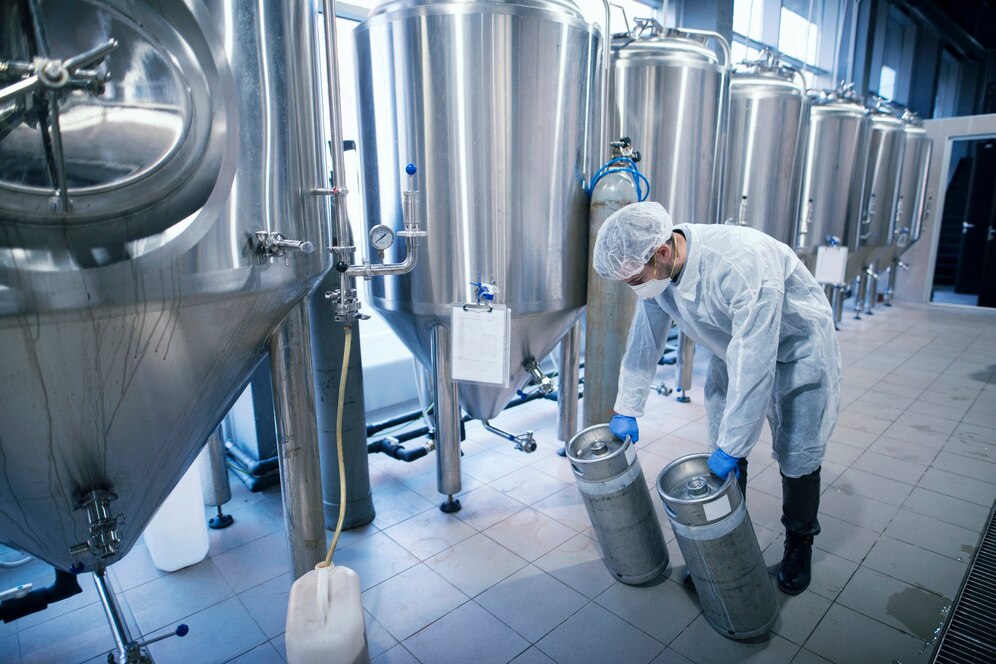

Fermentation tanks (Brewery).
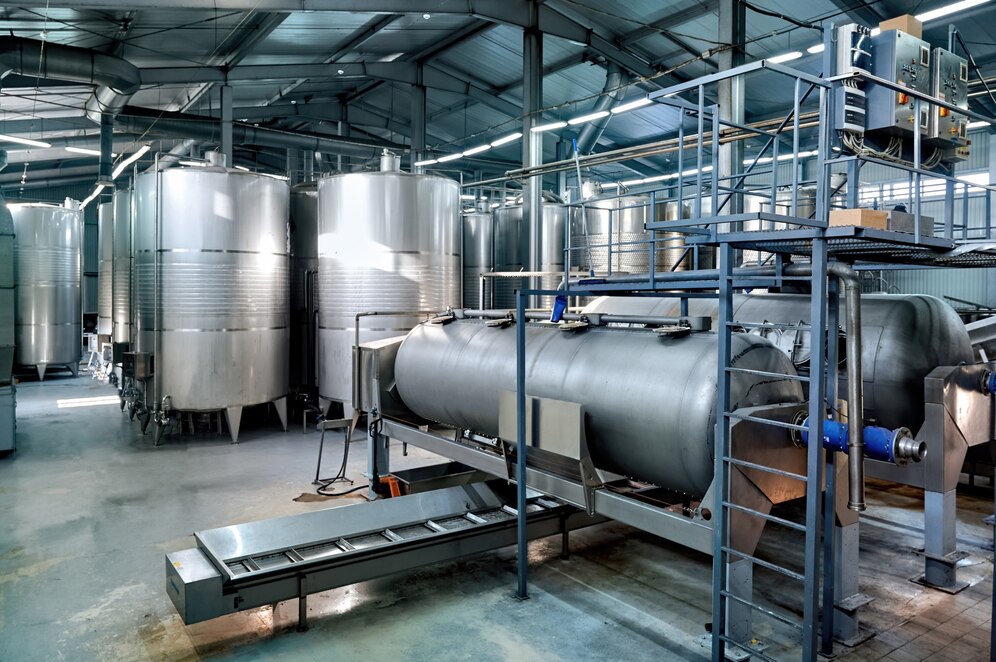

Reactors.
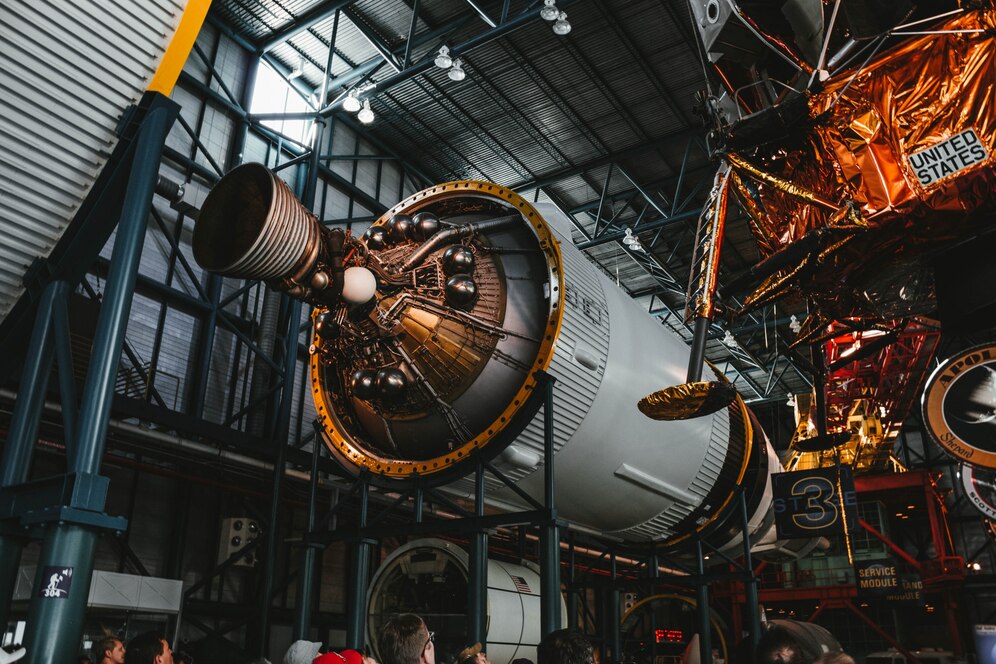
Aerospace industry
The aerospace industry comprises the activities involved in the research, design, manufacture and operation of aircraft, rockets and other air and space transportation vehicles. The sector covers a vast field of activities, with possible application in the military, industrial and commercial areas.

Steel industry
Steel mills are processing centers where iron ore is transformed into molten iron before going on to produce steel.
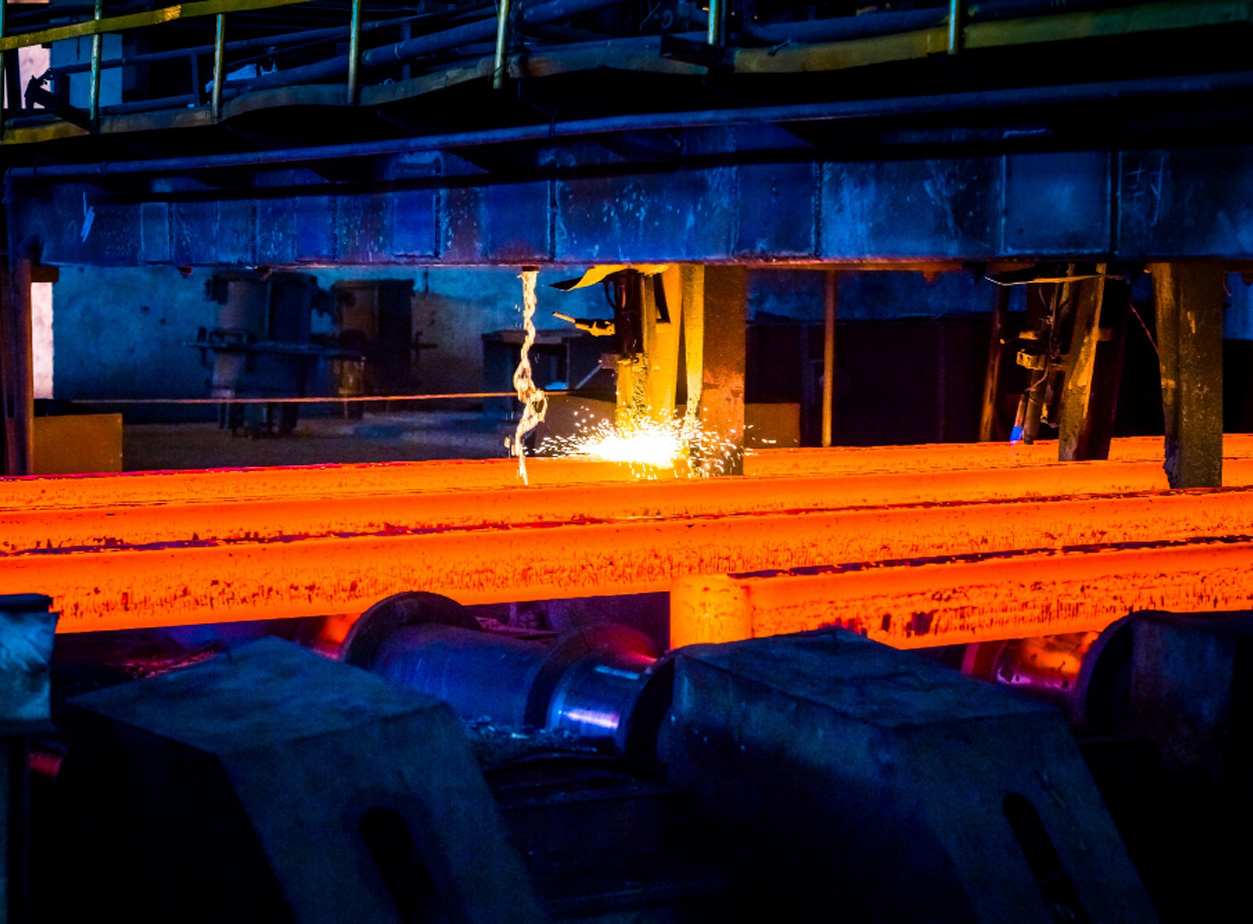


Steel fabrication and treatment.
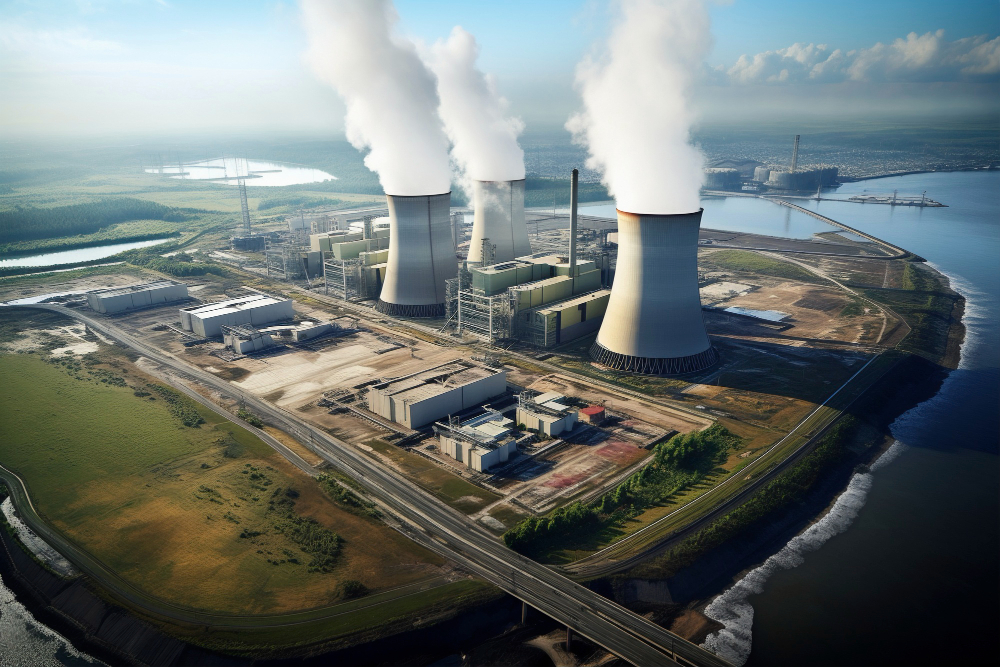
Nuclear Desalination
Desalination is the process by which the mineral salts dissolved in water are removed. Currently, this process, applied to seawater, is one of the most widely used to obtain fresh water for human or agricultural consumption.

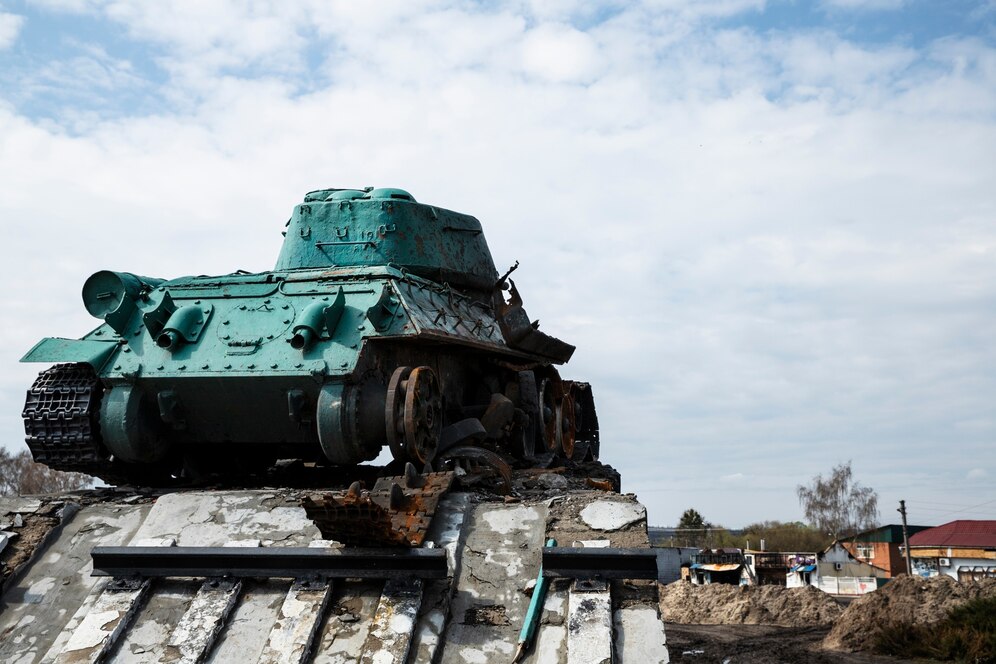
War industry
The war industry is the global trade aimed at the production of weapons, equipment and military technology, in particular arms, ammunition, missiles, military aircraft, military vehicles, ships and electronic systems.

Transport
The transportation industry consists of heavy trucks, aerospace, railways, locomotives, recreational vehicles, boats, containers, bridges and includes the maintenance of these products.